Watering a garden without a hose may seem daunting, but with ingenuity and sustainable practices, it can be both efficient and environmentally friendly. In today’s world, conserving water is more important than ever, and finding alternative methods to keep your garden hydrated can make a significant difference. Whether you’re facing water restrictions, aiming to reduce your water bill, or simply adopting more eco-friendly gardening practices, there are numerous ways to ensure your plants receive the moisture they need without relying on a traditional hose.
The possibilities are vast and varied, from manual watering techniques like watering cans and buckets to innovative solutions such as rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation systems. Additionally, understanding your garden’s specific water needs, improving soil moisture retention, and implementing intelligent landscaping strategies can all contribute to a thriving, lush garden.
In this guide, we’ll explore these sustainable watering methods in detail, helping you create a beautiful garden while conserving this precious resource.
Importance of Watering a Garden
Watering a garden is crucial for plant health and growth. Plants need water to perform essential functions like photosynthesis, nutrient transport, and cell structure maintenance. Without adequate water, plants wilt, become stressed, and are more susceptible to diseases and pests. Consistent watering ensures plants develop robust root systems, produce vibrant flowers, and yield bountiful harvests. Additionally, proper watering helps maintain soil structure and prevents issues like soil compaction and erosion.
It’s not just about survival; well-watered plants thrive, displaying their full beauty and potential. Regular watering also supports beneficial microorganisms in the soil, contributing to a healthier ecosystem. Whether growing vegetables, flowers, or ornamental shrubs, the right water is critical to achieving a thriving garden. Understanding the specific water needs of different plants and adjusting your watering practices accordingly can make a significant difference in your garden’s overall health and success.
Challenges of Watering Without a Hose

Watering a garden without a hose presents several challenges:
- It can be labor-intensive, requiring you to carry water manually using cans or buckets, which can be time-consuming and physically demanding, especially for more extensive gardens.
- Achieving even and consistent watering is more difficult without a hose, as controlling water distribution is more complex. This can lead to some areas being overwatered while others remain dry.
- Manual watering methods often result in more water evaporation, particularly during hot weather, making it less efficient. Collecting and transporting water from alternative sources like rain barrels or indoor taps can pose logistical challenges.
- Without the convenience of a hose, it’s harder to reach plants in distant or elevated spots.
Despite these challenges, a well-hydrated garden can be maintained with proper planning and innovative techniques, but extra effort and strategic thinking are required to overcome these obstacles effectively.
Manual Watering Methods
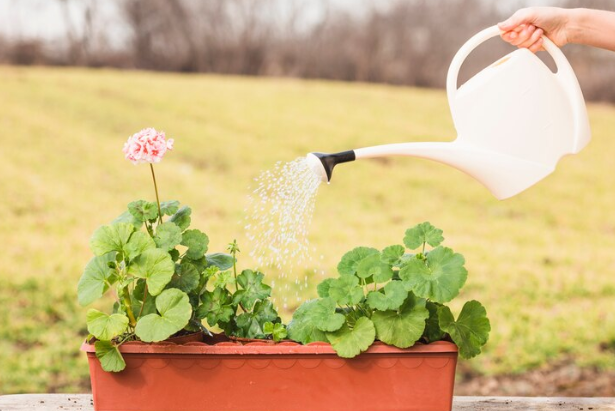

Manual watering methods are essential techniques for gardeners who do not have access to hoses or prefer a more hands-on approach to caring for their plants. These methods involve directly applying water to plants using various tools such as watering cans, buckets, or even handheld sprayers. Both methods require careful attention to avoid overwatering or under-watering plants, ensuring each plant receives adequate moisture to thrive.
Watering Cans:
Watering cans are famous for their simplicity and ease of use. They typically feature a spout and handle, allowing precise control over where and how much water is dispensed. Choosing the proper watering can involve considering factors like capacity, weight when full, and the type of nozzle for optimal water distribution. Techniques for efficient watering can include targeting the base of plants to minimize water loss through evaporation and ensuring thorough coverage without creating runoff.
Buckets and Containers:
Buckets and large containers are versatile and suitable for gardens with varying water needs. They can transport water from a water source to the garden and come in handy for watering larger plants or areas that require more water. DIY enthusiasts can also convert buckets into makeshift watering devices by adding small holes to the bottom, facilitating slow and steady water release directly into the soil.
Natural Watering Techniques

Natural watering techniques leverage environmental factors and resources to provide water to your garden without relying on traditional methods like hoses or manual watering tools. These techniques are not only eco-friendly but can also be highly effective in maintaining plant health and conserving water.
Rainwater Harvesting:
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater from roofs or other surfaces for later use in the garden. This method reduces reliance on municipal water supplies and provides plants with natural, untreated water free from chemicals like chlorine. Setting up a rain barrel or a more extensive rainwater collection system allows you to capture and store rainwater efficiently. This stored water can then be used during dry spells to supplement your garden’s watering needs.
Dew and Condensation Collection:
Dew and condensation can also contribute to watering your garden, especially in cooler climates or early mornings. Placing materials like cloths or plastic sheets overnight can collect dew, which can be wrung out and used to hydrate plants. While this method yields smaller amounts of water than rainwater harvesting, it can still be beneficial in arid regions or supplement other watering methods.
What Can I Use Instead of a Garden Hose?
Several effective options exist if you’re looking for alternatives to a garden hose. Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing waste. Soaker hoses, which slowly release water along their length, can be placed on the soil surface or buried under mulch for efficient watering. Watering cans are great for small gardens, allowing precise water delivery. Rain barrels collect rainwater that can be used later, conserving water and reducing costs. Wicking beds use capillary action to draw water from a reservoir into the soil, ensuring consistent moisture levels. Finally, automated sprinkler systems can be programmed to water specific areas at set times, providing convenience and efficiency. Each method offers unique benefits so you can choose the best one for your garden’s needs.
Innovative Watering Solutions
In today’s world, efficient and effective watering solutions are more critical than ever. As water scarcity becomes a growing concern, innovative watering systems can help conserve water and ensure that plants receive the right amount of moisture. This article explores two innovative watering solutions: drip irrigation systems and wicking beds.
Drip Irrigation Systems
Setting Up a Simple Drip System
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient method of watering plants by delivering water directly to the root zone. Setting up a simple drip system can be straightforward:
- Plan Your Layout: Identify the areas in your garden that need watering and map out where the drip lines will go.
- Gather Materials: You’ll need a water source, drip lines or tubing, emitters, connectors, and a timer.
- Install the Main Line: Connect the main line to your water source and lay it out according to your plan.
- Add Emitters: Attach emitters to the drip lines at the locations where you want water to be released.
- Connect to Water Source: Attach the main line to your water source and set up a timer to control watering times.
Advantages of Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation offers several benefits:
- Water Efficiency: Drip systems reduce waste by delivering water directly to the roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
- Improved Plant Health: Consistent and precise watering helps maintain optimal soil moisture levels, promoting healthy plant growth.
- Reduced Weed Growth: By targeting the root zone, drip irrigation limits water availability to weeds, reducing their growth.
- Cost Savings: Efficient water use can lead to lower water bills and reduced labour costs for manual watering.
Wicking Beds
How Wicking Beds Work
Wicking beds are an innovative solution that uses capillary action to draw water from a reservoir into the soil, providing consistent moisture to plants. Here’s how they work:
- Reservoir Layer: The bottom layer of the wicking bed is a water reservoir, typically lined with a waterproof material.
- Wicking Material: A layer of wicking material, such as gravel or sand, is placed above the reservoir to facilitate water movement.
- Soil Layer: The top layer consists of soil where plants are grown. Water is drawn up from the reservoir through the wicking material to moisten the soil.
- Overflow System: An overflow pipe is installed to prevent overfilling the reservoir and ensure excess water drains away.
Building Your Own Wicking Bed
Building a wicking bed can be a fun and rewarding project. Here’s a simple guide:
- Choose a Container: Select a suitable container, such as a large planter or raised garden bed, with enough depth to accommodate the reservoir and soil layers.
- Create the Reservoir: Line the bottom of the container with a waterproof liner and add a layer of gravel or sand to act as the wicking material.
- Install the Overflow Pipe: Insert an overflow pipe to manage excess water and prevent overfilling.
Conserving Water in the Garden
Water is a precious resource, and conserving it in the garden is crucial for sustainable gardening. Understanding the best times to water, recognizing signs of water needs, avoiding overwatering, and utilizing water-saving techniques can make your garden thrive while minimizing water usage.
Timing and Frequency of Watering
Best Times to Water Your Garden
The best times to water your garden are early in the morning or late in the afternoon. Watering during these times reduces evaporation, allowing more water to reach the plant roots. Morning watering is particularly beneficial as it will enable plants to absorb water before the day’s heat sets in.
Signs Your Garden Needs Water
Recognizing when your garden needs water is critical to maintaining plant health. Look for signs such as wilting leaves, dry soil, and reduced plant growth. Some plants, like succulents, may show signs of dehydration differently, such as wrinkling or colour changes.
Avoiding Overwatering
Overwatering can be as harmful as underwatering. Signs of overwatering include yellowing leaves, root rot, and mold growth on the soil surface. To avoid overwatering, ensure your garden has good drainage, and use a moisture meter to check soil moisture levels and water deeply but infrequently.
Using Greywater
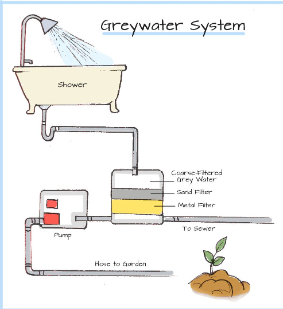
What is Greywater?
Greywater is gently used water from household activities such as laundry, dishwashing, and bathing. Unlike blackwater from toilets, greywater is relatively clean and can be recycled for irrigation and landscaping purposes. Reusing greywater helps conserve fresh water and reduces the strain on sewage systems. However, it’s essential to avoid using greywater that contains harmful chemicals or excessive salts. For safe usage, filter and treat greywater and apply it to non-edible plants, ensuring it doesn’t come into direct contact with the plant leaves or fruits.
How to Safely Use Greywater
To use greywater safely, follow these guidelines:
- Avoid Harmful Substances: Ensure greywater doesn’t contain harmful chemicals or high levels of salts. Use biodegradable and plant-friendly soaps and detergents.
- Filter and Treat: Filter greywater to remove particles and consider simple treatment methods to reduce pathogens.
- Apply to Non-Edible Plants: Use greywater primarily on ornamental plants and shrubs rather than edible plants to minimize health risks.
- Avoid Direct Contact: Apply greywater to the soil and avoid splashing it on plant leaves or edible parts.
Water-Saving Gardening Techniques
Plant Selection
Choosing the right plants can significantly reduce water usage. Opt for drought-tolerant and native species adapted to your local climate and requiring less water. Group plants with similar water needs together to ensure efficient watering.
Landscape Design
Effective landscape design can enhance water conservation. Implement the following strategies:
- Mulching: Use mulch to retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
- Zoning: Create watering zones based on plant water needs, ensuring each zone receives the appropriate amount of water.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Install rain barrels to collect and store rainwater for later use in the garden.
- Drip Irrigation: Use drip irrigation systems to deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing waste.
FAQ
What is the best time to water my garden?
The best time to water your garden is early in the morning or late in the afternoon. This reduces evaporation and ensures that water reaches the plant roots efficiently.
How can I tell if my garden needs water?
Wilting leaves, dry soil, and slow plant growth are signs that your garden needs water. Some plants may show specific signs, such as colour changes or leaf curling.
What types of plants are best for water conservation?
Drought-tolerant and native plants are ideal for water conservation. These plants are adapted to local climates and require less water to thrive.
How can I use greywater safely in my garden?
Use greywater safely, avoid harmful chemicals, filter and treat the water, and apply it to non-edible plants. Ensure greywater doesn’t come into contact with plant leaves or edible parts.
What are the benefits of mulching?
Mulching helps retain soil moisture, suppresses weeds, and regulates soil temperature. Organic mulch also improves soil health as it decomposes, adding nutrients to the soil.
Conclusion
Conserving water in the garden is essential for sustainable gardening and plant health. You can significantly reduce water usage by selecting drought-tolerant plants, using mulch, implementing drip irrigation, harvesting rainwater, improving soil quality, and practising intelligent watering techniques. These strategies conserve resources and promote a thriving, resilient garden. Embrace these water-saving techniques to ensure your garden remains beautiful and sustainable, even in dry conditions.
Read also: Can I Use Outdoor Soil for Indoor Plants? Safe planting







